Retrieval-Augmented Generation for AI-Generated Content: A Survey
Retrieval-augmented generation for AI-generated content has quickly become one of the most important advances in modern artificial intelligence. As large language models grow more powerful, they also face clear limitations: outdated knowledge, hallucinated facts, and a lack of transparency in how answers are formed. Retrieval-augmented generation, often shortened to RAG, addresses these challenges by combining generative models with real-time information retrieval. This survey explores the core concepts, technical foundations, and evolving research trends shaping RAG systems today. For a comprehensive overview of RAG methodology, see the original research paper on arXiv.
- Understanding the Problem with Purely Generative AI
- What Is RAG? A Clear Definition
- Core Architecture of Retrieval-Augmented Generation
- Why Retrieval-Augmented Generation Improves AI-Generated Content
- RAG vs Fine-Tuning: A Practical Comparison
- Research Trends in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
- Evaluation Challenges in RAG Systems
- Real-World Applications of Retrieval-Augmented Generation
- The Future of Retrieval-Augmented Generation
- Frequently Asked Questions
Whether you are a researcher, developer, or decision-maker exploring applied AI, understanding how retrieval-augmented generation works — and why it matters — is essential for building trustworthy, up-to-date AI-generated content. Learn more about AI research tools for advanced projects.
Understanding the Problem with Purely Generative AI
Traditional generative AI models, including large language models, are trained on massive datasets and generate responses based on learned patterns. While impressive, this approach has structural weaknesses:
- Static knowledge: Models only know what existed during training.
- Hallucinations: Confident but incorrect information can be produced.
- Lack of verifiability: Sources are rarely explicit.
- Domain limitations: Specialized or proprietary knowledge is often missing.
These issues become critical in enterprise systems, academic research, healthcare, legal analysis, and any scenario where accuracy matters. This is where retrieval-augmented generation enters the picture.
What Is RAG? A Clear Definition
What is RAG? Retrieval-augmented generation is a hybrid AI framework that enhances text generation by retrieving relevant external information before producing a response. Instead of relying solely on internal model knowledge, RAG systems fetch documents, passages, or data from external sources and use them to guide generation.
In simple terms, RAG follows a two-step process:
- Retrieve: Search a knowledge base or document store for relevant information.
- Generate: Use the retrieved content to produce a grounded, informed response.
This design significantly improves factual accuracy, contextual relevance, and trustworthiness in AI-generated content.
Core Architecture of Retrieval-Augmented Generation
The architecture of retrieval-augmented generation typically consists of three major components, as detailed in our AI architecture guide for modern systems.
1. Knowledge Source
The knowledge source can include structured databases, unstructured documents, PDFs, research papers, web pages, or internal enterprise data. This flexibility allows RAG systems to operate across many domains.
2. Retriever Model
The retriever is responsible for finding relevant information. It often uses vector embeddings and similarity search techniques to match user queries with the most relevant content. Modern retrievers rely on dense vector representations rather than keyword matching.
3. Generator Model
The generator is usually a large language model that synthesizes retrieved information into a coherent response. The retrieved documents act as contextual grounding, reducing hallucinations and improving accuracy.
This modular architecture is a major reason why retrieval-augmented generation scales well across applications.
Why Retrieval-Augmented Generation Improves AI-Generated Content
Retrieval-augmented generation for AI-generated content offers several practical advantages over traditional generative approaches:
- Factual grounding: Responses are tied to real documents.
- Up-to-date information: Knowledge bases can be refreshed without retraining models.
- Transparency: Retrieved sources can be shown or audited.
- Domain adaptability: Works well with specialized or proprietary data.
These strengths make RAG especially valuable in professional and high-stakes environments.
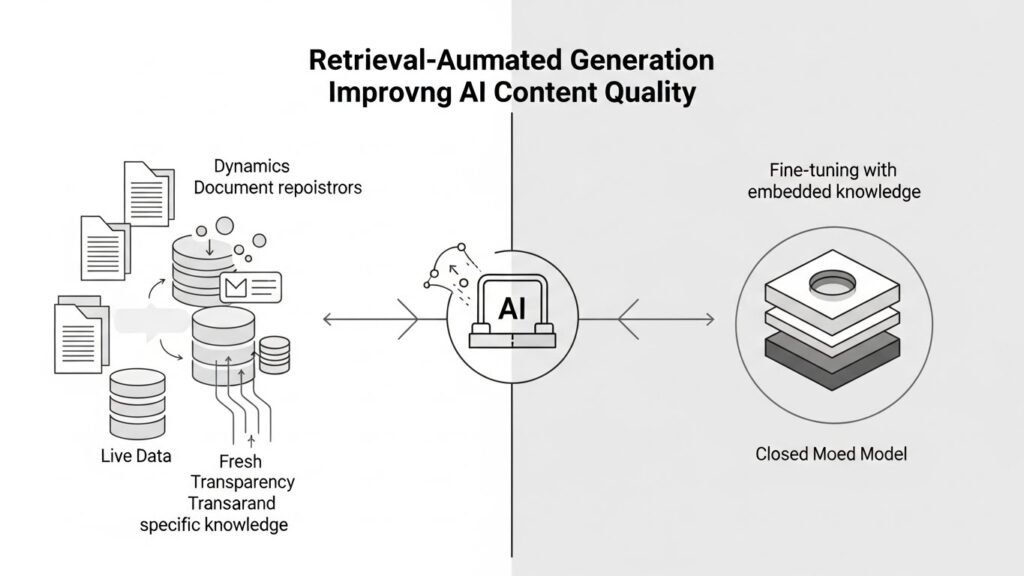
RAG vs Fine-Tuning: A Practical Comparison
Fine-tuning and retrieval-augmented generation are often compared, but they serve different purposes:
- Fine-tuning embeds knowledge directly into model weights, requiring retraining.
- RAG keeps knowledge external, allowing fast updates and flexible control.
Many modern systems combine both approaches, but RAG remains the preferred solution when data changes frequently or explainability is important.
Research Trends in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Academic and industry research on RAG has grown rapidly. A review of the retrieval augmented generation journal landscape reveals several emerging trends:
Improved Retrieval Techniques
Researchers are exploring hybrid retrievers that combine dense vectors with symbolic search, improving recall and precision across diverse datasets.
End-to-End Optimization
Rather than treating retrieval and generation separately, newer models optimize both components jointly, improving overall system performance.
Faithfulness and Attribution
Ensuring that generated outputs accurately reflect retrieved sources is a key research focus. Attribution methods help link generated text to specific documents.
Multimodal RAG
Beyond text, RAG systems are being extended to images, tables, audio, and video, opening new research directions.
Evaluation Challenges in RAG Systems
Evaluating retrieval-augmented generation is more complex than evaluating pure language models. Metrics must consider:
- Retrieval accuracy
- Generation faithfulness
- Answer completeness
- Source alignment
This has led to new benchmarks and evaluation frameworks specifically designed for RAG pipelines.
Real-World Applications of Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Retrieval-augmented generation for AI-generated content is already being deployed across industries:
- Enterprise search: Internal knowledge assistants
- Customer support: Accurate, policy-based responses
- Research assistance: Literature review and summarization
- Healthcare and legal: Evidence-grounded explanations
These applications highlight why RAG is considered a foundational technology rather than a niche technique. Discover more about enterprise AI solutions for practical use.
Limitations and Open Research Questions
Despite its strengths, retrieval-augmented generation is not without challenges:
- Latency from retrieval steps
- Dependence on data quality
- Complex system design
- Risk of irrelevant or biased retrievals
Ongoing research aims to address these limitations through better retrievers, smarter filtering, and improved generation controls.
The Future of Retrieval-Augmented Generation
The future of retrieval-augmented generation points toward more adaptive, explainable, and multimodal systems. As AI moves from experimental tools to trusted infrastructure, RAG will play a central role in ensuring accuracy and accountability.
Rather than replacing language models, retrieval-augmented generation complements them, forming a practical bridge between learned intelligence and real-world knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is retrieval-augmented generation in simple terms?
Retrieval-augmented generation is a method where an AI system searches for relevant information first and then uses that information to generate accurate responses.
Why is RAG important for AI-generated content?
RAG reduces hallucinations, keeps information up to date, and improves trust by grounding responses in real data sources.
How does RAG differ from traditional AI models?
Traditional models rely only on training data, while RAG systems dynamically retrieve external information during generation.
Is retrieval-augmented generation widely researched?
Yes, retrieval augmented generation journal publications have increased significantly, reflecting strong academic and industry interest.
Can RAG be used with proprietary data?
Absolutely. One of RAG’s strengths is its ability to securely work with private or domain-specific knowledge bases.







