How Google Checks Backlinks to Help Measure Domain Authority Accurately
Understanding how Google checks backlinks is one of the most important pieces of the SEO puzzle. Backlinks are not just links pointing to your site; they are signals of trust, relevance, and website authority in SEO.
. When Google evaluates a website, it looks closely at its backlink profile to decide how credible and valuable that site is compared to others. This process plays a major role in how search rankings and overall domain authority are shaped.
Many website owners know backlinks matter, but fewer truly understand how Google analyzes them and how to use a domain authority checker effectively.
In this guide, we’ll break everything down in clear, simple terms so you can fully understand how backlinks influence domain authority and how to evaluate them properly.
What Are Backlinks and Why Do They Matter to Google
A backlink is simply a link from one website to another. From Google’s perspective, backlinks act like votes. When a reputable website links to your content, it’s essentially telling Google, “This page is worth trusting.”
- What Are Backlinks and Why Do They Matter to Google
- How Google Checks Backlinks Behind the Scenes
- Does Google Use “Domain Authority” Directly?
- Key Backlink Factors Google Values Most
- How Google Detects Unnatural or Spammy Backlinks
- How SEO Tools Estimate Backlinks and Domain Authority
- How to Check Backlinks Effectively
- Free Backlink Checker Tools: What They Can and Can’t Do
- Why Domain Authority Is Still Useful for SEO Decisions
- Common Myths About Google and Backlinks
- FAQ
However, not all votes carry the same weight. Google doesn’t just count backlinks; it evaluates their quality, relevance, and context. A single link from a highly authoritative site can be more valuable than dozens of low-quality links.
Backlinks help Google in three major ways:
- Discovering new pages: Google finds content by following links.
- Understanding relevance: Links provide context about what a page is about.
- Measuring authority: Links help determine how trustworthy a site is.
How Google Checks Backlinks Behind the Scenes
Google uses automated systems called crawlers (or bots) to scan the web continuously, which you can learn more about in this official guide to Google crawlers.
These crawlers follow links from page to page, collecting data about where links come from, where they point, and how they are placed.
When Google checks backlinks, it looks at multiple factors, including:
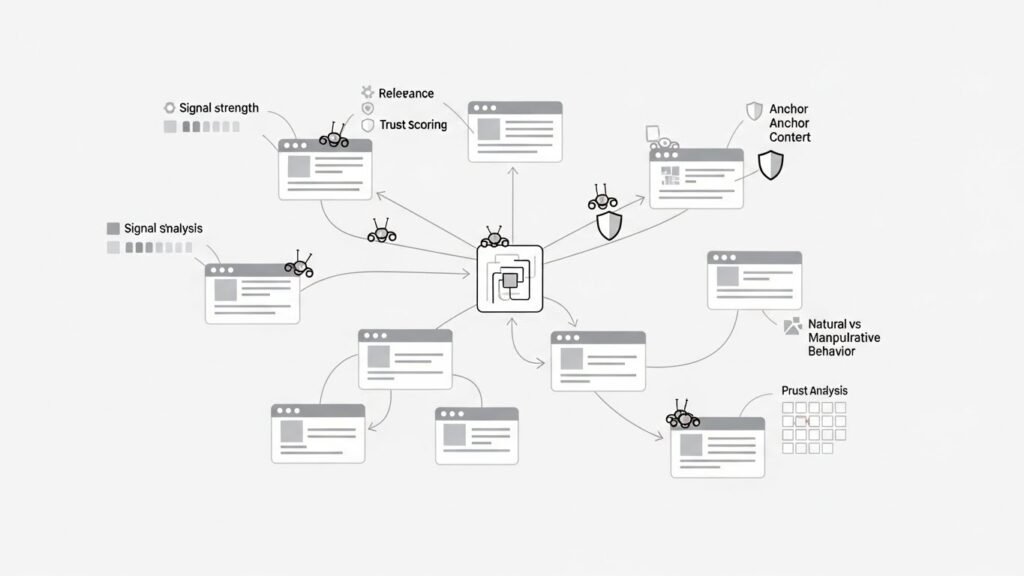
- The authority of the linking website
- The relevance of the linking page to your content
- The anchor text used in the link
- Whether the link is natural or manipulative
- The overall link pattern of your site
This data is processed by Google’s algorithms to help determine how much trust and authority your site deserves.
Does Google Use “Domain Authority” Directly?
This is a common point of confusion. Google does not use a metric called “Domain Authority” in its ranking algorithm. Domain Authority is actually a third-party metric created by SEO tool providers to estimate how strong a domain is based on backlink data.
That said, the concept behind domain authority aligns closely with how Google evaluates websites. Google measures authority, just not under that specific name. It relies on complex scoring systems that analyze backlink quality, relevance, and consistency over time.
So when you use a domain authority checker, you’re not seeing Google’s internal score. You’re seeing an approximation based on publicly observable link signals.
Key Backlink Factors Google Values Most
1. Link Quality Over Quantity
Google strongly prefers high-quality links over sheer numbers. A link from a respected publication, industry blog, or educational site carries far more weight than dozens of links from unknown or spammy pages.
2. Relevance of the Linking Site
If your website is about software tools, a backlink from a relevant tech or marketing site for backlinks is far more valuable than one from an unrelated niche.
Relevance helps Google understand your topical authority.
3. Anchor Text Context
Anchor text is the clickable text in a link. Google analyzes it to understand what the linked page is about. Natural, descriptive anchor text is preferred over over-optimized or keyword-stuffed anchors.
4. Link Placement
Links placed naturally within the main content of a page are generally more valuable than links in footers, sidebars, or author bios.
5. Follow vs Nofollow Links
“Follow” links pass authority signals, while “nofollow” links typically do not. However, nofollow links can still provide indirect value through traffic and brand exposure.
How Google Detects Unnatural or Spammy Backlinks
Google is very good at identifying link manipulation. Practices like buying links, using private blog networks, or mass directory submissions are easily detected over time.
Some red flags Google looks for include:
- Sudden spikes in backlinks from low-quality sites
- Repetitive, keyword-heavy anchor text
- Links from irrelevant or foreign-language domains
- Large numbers of links from the same IP ranges
When detected, these links are either ignored or can negatively affect your site’s trust signals.
How SEO Tools Estimate Backlinks and Domain Authority
Since Google’s internal data isn’t public, SEO tools build their own web indexes. They crawl billions of pages, track links, and apply proprietary formulas to estimate authority.
A typical domain authority checker uses:
- Total number of referring domains
- Authority of those referring domains
- Link diversity
- Spam indicators
These tools are extremely useful for comparison and trend analysis, even if they don’t perfectly match Google’s internal systems.
How to Check Backlinks Effectively
To understand your backlink profile, you need to look beyond simple counts. When you check backlinks, focus on patterns and quality.
Key things to review include:
- Which domains link to you most often
- The authority level of linking sites
- Anchor text distribution
- New vs lost backlinks over time
This helps you spot growth opportunities as well as potential risks.
Free Backlink Checker Tools: What They Can and Can’t Do
Free backlink checker tools are popular because they offer quick insights without cost. They are ideal for beginners, small websites, and initial audits.
Benefits of free tools:
- Quick overview of backlink profile
- Basic domain authority estimates
- Identification of top linking domains
Limitations to keep in mind:
- Smaller link databases
- Limited historical data
- Restricted export or filtering options
While free tools are helpful, serious SEO work often requires combining insights from multiple sources.
Why Domain Authority Is Still Useful for SEO Decisions
Even though Google doesn’t use domain authority directly, it remains a valuable benchmarking metric. It helps you:
- Compare your site against competitors
- Evaluate link-building opportunities
- Track authority growth over time
When used correctly, domain authority becomes a directional indicator rather than an absolute score.
Common Myths About Google and Backlinks
More Links Always Mean Better Rankings
This is false. Low-quality links can be ignored or even harmful.
New Sites Can’t Build Authority
New sites can earn authority quickly with strong content and relevant links.
All Nofollow Links Are Useless
No-follow links still contribute to a natural link profile and visibility.
FAQ
How often does Google check backlinks?
Google crawlers continuously scan the web, so backlink data is updated regularly, though not always in real time.
Is domain authority an official Google ranking factor?
No, domain authority is a third-party metric, but it reflects factors Google does care about.
Can bad backlinks hurt my website?
Most low-quality links are ignored, but large-scale manipulative link patterns can reduce trust signals.
Are free backlink checker tools accurate?
They are useful for basic insights but may not show a complete backlink profile.
What is the best way to improve backlink quality?
Creating valuable, relevant content and earning links naturally from trusted sites is the most reliable approach.







