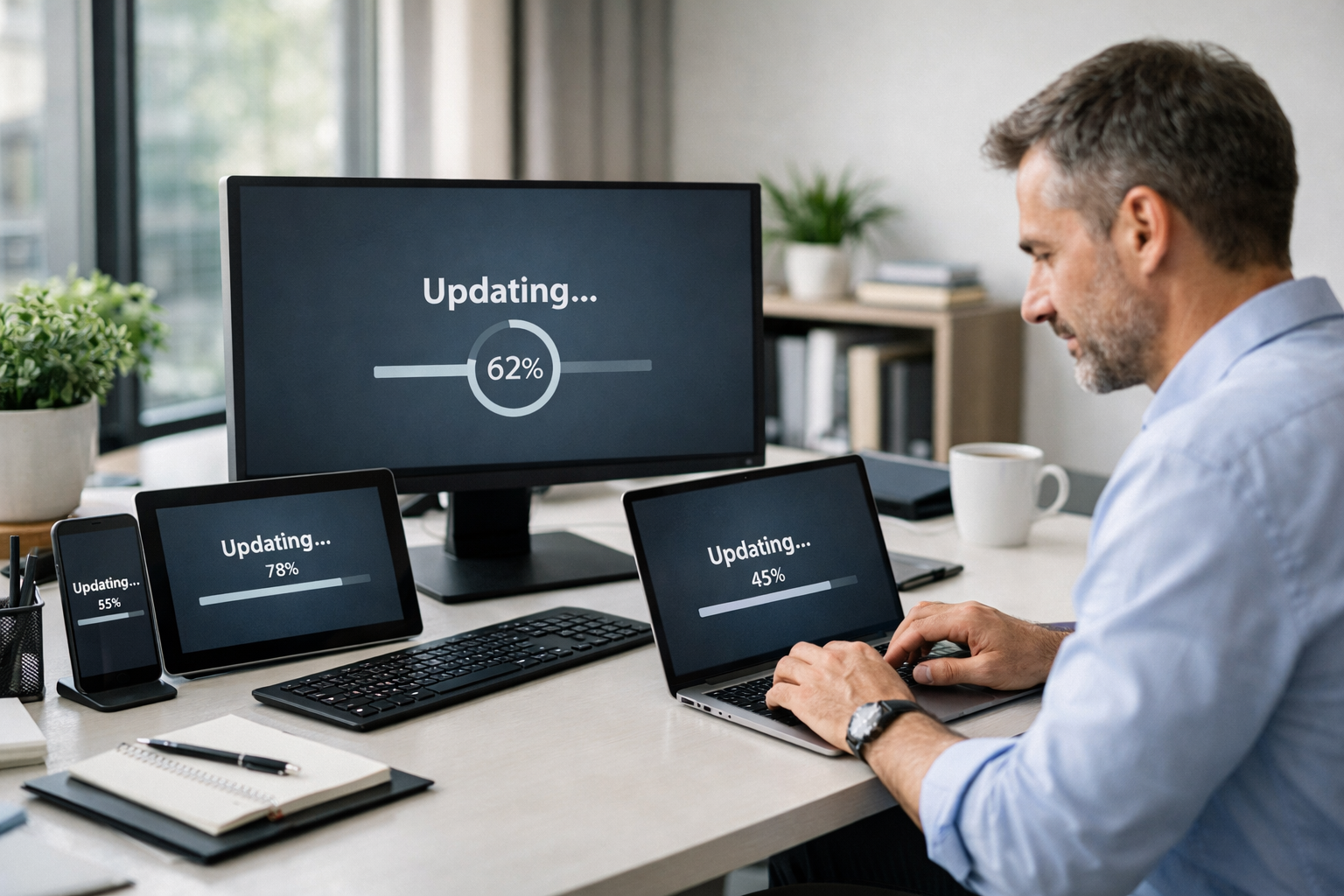
In today’s fast-paced digital world, keeping your systems updated is no longer optional—it’s essential. The best patch management software helps businesses and individuals maintain optimal performance, prevent security risks, and reduce downtime, similar to how IT monitoring tools improve system oversight.
If you’ve ever wondered how patch updates affect your devices or what tools can simplify the process, this guide will give you clear, actionable insights.
What is Patch Management?
Before diving into software solutions, it’s important to understand what patch management actually is, as defined by CISA’s official patch management guide.
Patch management is the process of identifying, acquiring, testing, and installing software updates (patches) for your operating systems, applications, and devices. These patches fix vulnerabilities, enhance features, and improve system stability.
Without proper patch management, your system can be exposed to bugs, crashes, and even cyberattacks. A structured patch management process ensures that updates are applied consistently, minimizing risk while boosting overall system performance.
- What is Patch Management?
- Why Patch Management Matters
- How the Best Patch Management Software Works
- Key Features to Look for in Patch Management Software
- Benefits of Using the Best Patch Management Software
- Best Practices for Effective Patch Management
- Common Challenges in Patch Management
- Top Tips for Choosing the Right Patch Manager
- FAQ
Why Patch Management Matters
Many organizations underestimate the importance of regular updates. Here’s why patch management is crucial:
- Security Protection: Patches often address known vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit. Without them, your system is at risk.
- System Stability: Updates fix bugs and software glitches that can slow down your devices.
- Compliance: Industries like healthcare and finance require up-to-date systems to meet regulatory standards.
- Performance Optimization: Well-maintained systems run faster and more efficiently.
How the Best Patch Management Software Works
A patch manager automates the entire patching process, saving time and reducing human error, much like software deployment tools streamline IT operations.
Here’s how it typically works:
- Scanning: The software scans your network for outdated software and missing patches.
- Assessment: It identifies critical updates and prioritizes them based on risk and relevance.
- Deployment: Patches are deployed automatically across all devices, often without interrupting user activity.
- Reporting: Detailed reports show which systems are updated, which failed, and why.
Key Features to Look for in Patch Management Software
Choosing the best patch management software involves understanding which features are essential for your environment, similar to considerations when selecting IT management software tools.
Here’s what to prioritize:
- Automation: Automatically scans and installs updates without manual intervention.
- Compatibility: Supports a wide range of operating systems, software, and devices.
- Scheduling: Allows patches to be applied during off-peak hours to avoid disruption.
- Reporting & Alerts: Provides real-time updates on patch status and compliance.
- Rollback Options: Let you revert updates if they cause issues.
Benefits of Using the Best Patch Management Software
Investing in a robust patch management solution provides several tangible benefits:
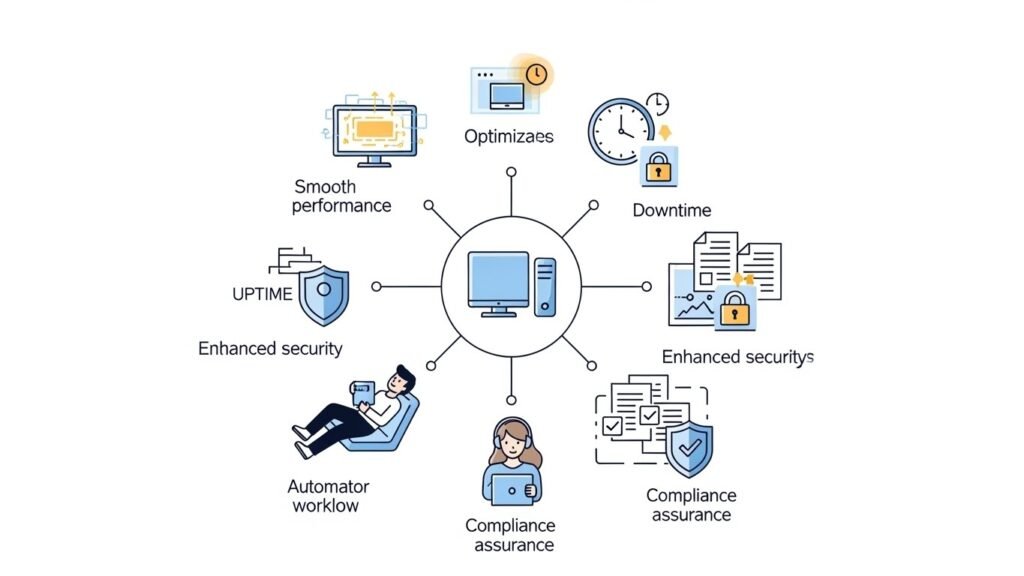
- Improved System Performance: Systems run more smoothly as bugs and glitches are resolved promptly.
- Reduced Downtime: Automated updates reduce the chances of unexpected crashes or failures.
- Enhanced Security: Minimizes exposure to malware and exploits by keeping software current.
- Time & Resource Savings: IT teams spend less time manually tracking and applying updates.
- Compliance & Peace of Mind: Ensures systems meet regulatory standards and internal policies.
Best Practices for Effective Patch Management
Even with the best patch management software, following best practices ensures maximum benefits:
- Regular Scanning: Set your patch manager to scan your systems frequently.
- Prioritize Critical Updates: Apply security patches first to minimize risk.
- Test Before Deployment: Use a small group of devices to test patches before full-scale deployment.
- Keep Backups: Ensure backups are up to date in case a patch causes unexpected issues.
- Monitor and Report: Continuously track patch status and review reports for compliance and coverage.
Common Challenges in Patch Management
Despite the benefits, patch management can be tricky. Some common challenges include:
- Legacy Systems: Older software may not be supported by modern patch managers.
- Compatibility Issues: Certain patches can conflict with existing software or configurations.
- Network Constraints: Large-scale deployments can strain network bandwidth if not scheduled properly.
- User Resistance: Automatic restarts or interruptions may frustrate users if not communicated.
Top Tips for Choosing the Right Patch Manager
To select the best patch management software for your needs, consider:
- Assessing your IT environment size and complexity
- Checking vendor support and update frequency
- Looking for intuitive dashboards and reporting tools
- Ensuring strong automation capabilities without compromising control
FAQ
What is patch management?
Patch management is the process of updating software to fix vulnerabilities, bugs, and performance issues. It ensures systems run securely and efficiently.
Why is patch management important?
It prevents security breaches, reduces system downtime, ensures compliance, and improves overall performance by keeping software up to date.
What does a patch manager do?
A patch manager automates the process of identifying, testing, and installing software updates across devices, minimizing manual work and errors.
Can patch management improve system performance?
Yes, by fixing software bugs and optimizing updates, patch management ensures that systems operate smoothly and efficiently.
How often should patches be applied?
Patches should be applied regularly, with critical security updates prioritized immediately. Routine scans and updates are recommended weekly or monthly, depending on the environment.
Are there risks to patch management?
While patch management is generally safe, poorly tested updates or compatibility issues can occasionally cause software conflicts or system instability. Using a reliable patch manager mitigates these risks.







